One of the situations most frequently faced by full backs in defensive situations is when they are equal or numerically inferior to their opponents. In order to solve this type of action, it is essential for defenders to master the defensive fundamental of ‘identifying the player to mark’.
In the following, we will detail the key aspects of the IFP, both in terms of describing the different situations that may occur, as well as explaining the optimal responses in each scenario.
Scenario 1
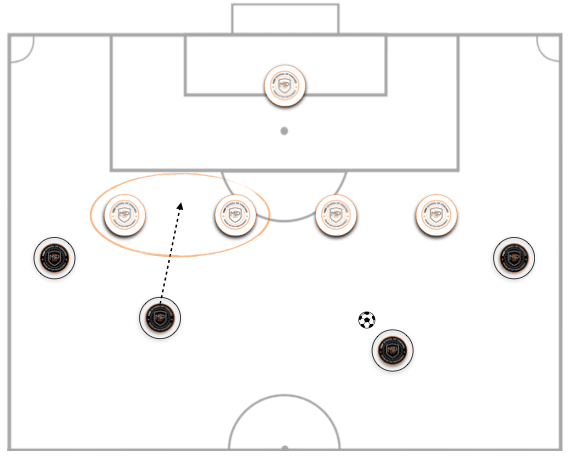
One of the most frequent circumstances of numerical equality faced by the full back is when two players, one with and one without possession of the ball, enter from the wing.
In this scenario, the defender must take responsibility for the attacker closest to the wing, while the centre-back takes responsibility for the player with the ball. In addition, the full back must be in a position to cover his teammate, in order to be able to intervene and stop the opponent’s advance if the centre back is beaten.
* Picture 1: Scenario 1. Numerical Equality. MBP School of Coaches
Scenario 2
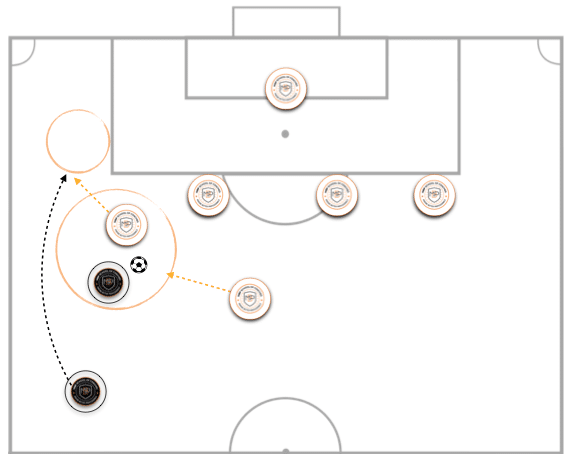
The second most frequent scenario is when a player in possession of the ball has two open passing lines in the wide channel: one attacking the intra-linear interval between the centre back and the full back, and the other positioned wide.
* Picture 2: Scenario 1. Numerical Equality. MBP School of Coaches
In this case, the defender must deal with the more dangerous attacker, i.e. the one attacking the gap, leaving the open player unmarked.
However, if there is a switch to towards the outside player, the full back must apply another fundamental to hinder the attacker receiving the ball.
Scenario 3
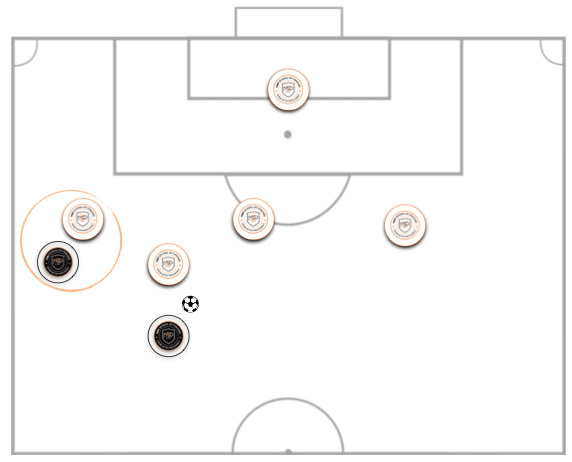
The last most common situation is when a player in possession is fixing the full back, while another player without the ball overlaps on the wing.
* Picture 3: Scenario 1. Numerical Inferiority. MBP School of Coaches
In this scenario, the defender must deal with the unmarked attacker, while being assisted by the winger or holding midfielder, who will be responsible for defending the attacker with the ball.
Conclusion
Knowing how to identify which player to mark depending on the situation is key for the full back to successfully perform defensive roles. Each scenario requires a high capacity to read the play, as it is made up of different factors to be taken into account. Therefore, it will be essential that the defender stands out for their cognitive structure, in addition to possessing an excellent defensive technical mastery, in order to resolve all actions successfully.
Do you want to know how your individual players should behave in different game situations?
At the MBP School of Coaches, we offer you an online course that will allow you to deepen your knowledge of more than 90 individual fundamentals by player position.
All these fundamentals are born from an exhaustive study of each and every one of the most common and relevant situations in which each player finds themselves in during a match depending on their position on the pitch. Once these situations in the game have been detected, we study which are the optimal responses that give the player the best chance of success.
In addition, you will have access to all the content related to the player structure that is taught in person in our Master in High Performance Football. All this will be available to the student online, providing an innovative teaching methodology through the use of gamification and the story of ‘La Quinta de Mati’.
What should the player focus on in order to make the best decision in each situation? How does the coach organise each of these fundamentals? What are the key points to the correct execution of these optimal responses? What details of the fundamentals are essential to improve the player’s tactical training?
Click here for all the answers